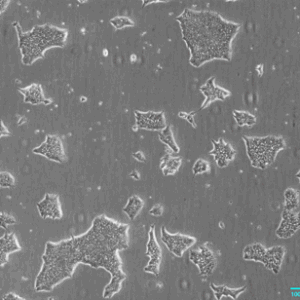
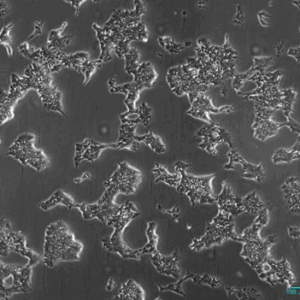
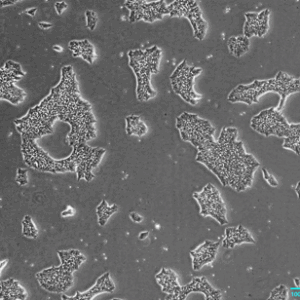
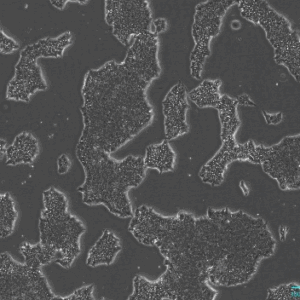
PluriBank™
We're thrilled to expand our PluriBank™ RUO portfolio with new, low-passage PluriBank™ RUO FailSafe® lines that features enhanced immune evasion through reduced T cell recognition and a selective ablation mechanism to remove dividing cells while preserving post-mitotic cells. This innovative line integrates mRNA-reprogrammed iPSCs with CRISPR-based knockouts of B2M and CIITA genes, plus the FailSafe safety switch. For flexibility, we also offer a sister line with only the FailSafe knock-in.
For consistent and reproducible culture of PluriBank™ RUO FailSafe® lines, Pluristyx recommends PluriKit™, a set of reagents tests and selected for their ability to maintain cell viability, pluripotency, and genomic integrity throughout culture and cryopreservation.
Comprehensive usage instructions are available in our Instructions for Use.
FailSafe
HSV-TK is a viral enzyme that processes the non-toxic ganciclovir pro-drug into a cytotoxic product. FailSafe cells have HSV-TK gene inserted into an essential cell division locus1. This provides researchers with a potent tool for time and dose-dependent ablation of dividing cells in culture while leaving post-mitotic cells intact. For cell therapy, the FailSafe cell system can be used as a safety switch that selectively eliminates dangerous proliferating cells while allowing post-mitotic therapeutic cells to remain and continue benefiting the patient.
B2M CIITA Knock out
The B2M gene is critical for MHC class I molecule expression, while CIITA is necessary for MHC class II expression. Removing B2M disrupts the presentation of antigens on MHC class I molecules, helping the transplanted cells evade detection by the recipient’s cytotoxic T cells. Similarly, knocking out CIITA prevents the expression of MHC class II molecules, which reduces the likelihood of recognition by helper T cells. Together, these knockouts minimize immune activation against transplanted cells, increasing their survival and functionality in the recipient. Knocking out B2M and CIITA, in conjunction with knocking in a gene to help cells evade innate immunity is used as the basis for several hypo-immune platforms 2,3.
Cell line
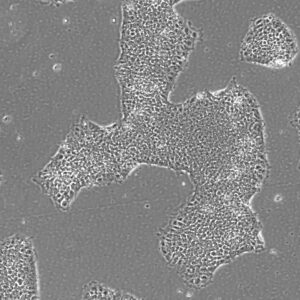
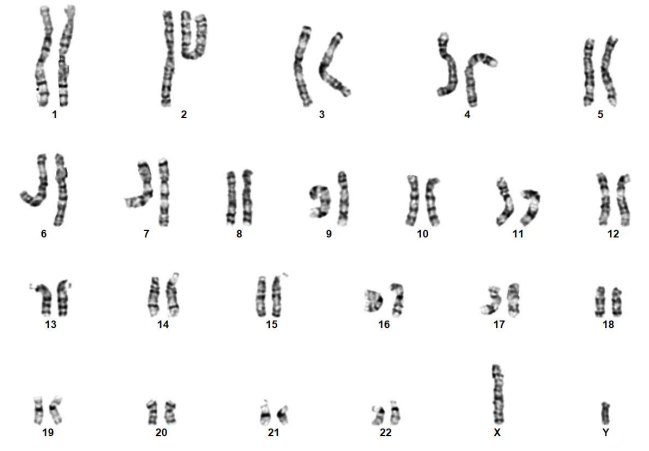
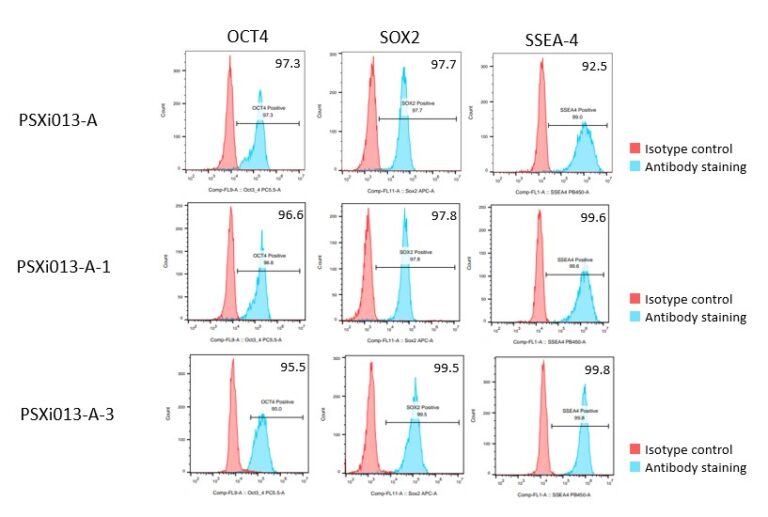
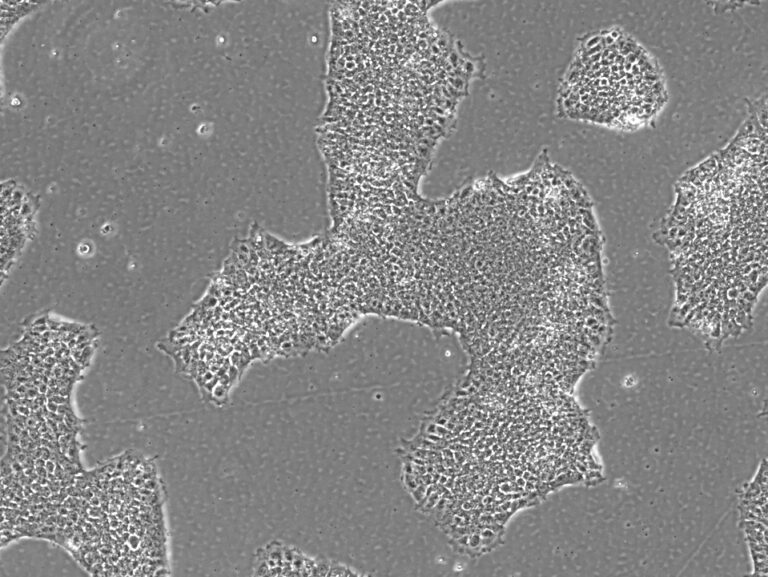
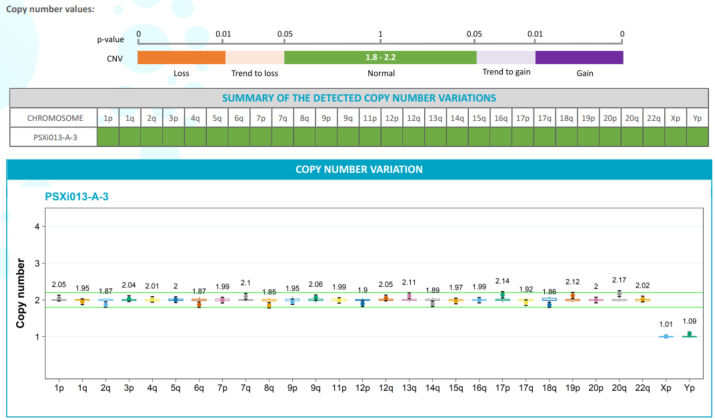
These edits are made available on the Pluristyx PSXi013 line: a male Caucasian fibroblast reprogrammed line using mRNA technology. PSXi013-A iPSCs have shown promising differentiation potential in the hands of partners and collaborators into islet cells, hepatocytes, CD34+ progenitors, NK cells, neurons, and cardiomyocytes.
-
PSX iPSC
PluriBank FailSafe R&D Vial
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
PSX iPSC
PluriBank FailSafe B2M/CIITA knockout R&D Vial
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
Figures:
References:
1Liang, Q., Monetti, C., Shutova, M.V. et al. Linking a cell-division gene and a suicide gene to define and improve cell therapy safety. Nature 563, 701–704 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0733-7
2Gornalusse GG, Hirata RK, Funk SE, Riolobos L, Lopes VS, Manske G, Prunkard D, Colunga AG, Hanafi LA, Clegg DO, Turtle C, Russell DW. HLA-E-expressing pluripotent stem cells escape allogeneic responses and lysis by NK cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2017 Aug;35(8):765-772. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3860. Epub 2017 May 15. PMID: 28504668; PMCID: PMC5548598.
3Hu, X., White, K., Olroyd, A.G. et al. Hypoimmune induced pluripotent stem cells survive long term in fully immunocompetent, allogeneic rhesus macaques. Nat Biotechnol 42, 413–423 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-023-01784-x
Unmodified iPSCs
Pluristyx is proud to offer off-the-shelf iPSCs for immediate evaluation. These iPSC lines are generated from our proprietary cellular reprogramming technology. Pluristyx's catalogue of stem cells are fully characterized to ensure pluripotency and genetic stability of the cells with a clinical application in mind.
iPSCs are generated from regulatory-compliant donors and can be evaluated to assist in the selection of lines appropriate for your research. Our portfolio of cell lines includes both research and GMP clinical grade cell lines.
-
PSC
PSXi005 - Female, 18 year old
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
PSC
PSXi007 - Male, 23 year old
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
PSC
PSXi008 - Male, 20 year old
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
PSC
PSXi009 - Female, 24 year old
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
PSC
PSXi010 - Female, 25 year old
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
PSC
PSXi011 - Female, 26 year old
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
PSC
PSXi012 - Male, 26 year old
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
PSC
PSXi013-E - Male, 60 year old
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
PSC
PSXi014 - Male, 30 year old
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
PSC
PSXi016 - Female, 18 year old
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
PSC
PSXi017 - Male, 26 year old
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page